一、什么是二叉树
1.概述
首先,需要了解树这种数据结构的定义:
树:是一类重要的非线性数据结构,是以分支关系定义的层次结构。每个结点有零个或多个子结点;没有父结点的结点称为根结点;每一个非根结点有且只有一个父结点;除了根结点外,每个子结点可以分为多个不相交的子树
树的结构类似现实中的树,一个父节点有若干子节点,而一个子节点又有若干子节点,以此类推。
2.名词解释
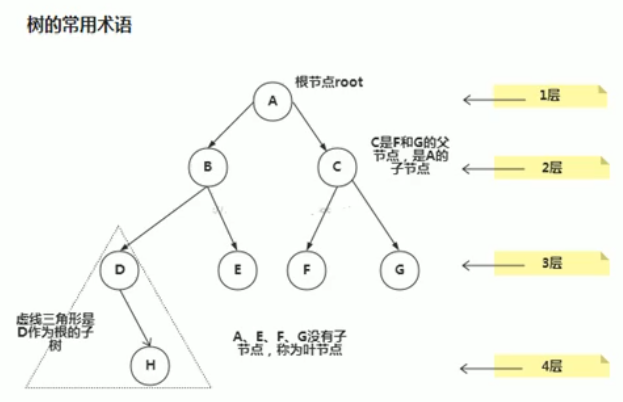
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 根节点 | 树的顶端结点 |
| 父节点 | 若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点 |
| 子节点 | 具有相同父节点的节点 |
| 兄弟节点 | 彼此都拥有同一个父节点的节点 |
| 叶子节点 | 即没有子节点的节点 |
| 节点的权 | 即节点值 |
| 路节点的度 | 一个节点含有的子树的个数 |
| 树的度 | 一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度 |
| 深度 | 根结点到这个结点所经历的边的个数 |
| 层数 | 该节点的深度+1 |
| 高度 | 结点到叶子结点的最长路径所经历的边的个数 |
| 树高度 | 即根节点的高度 |
| 森林 | 由m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林 |
3.二叉树
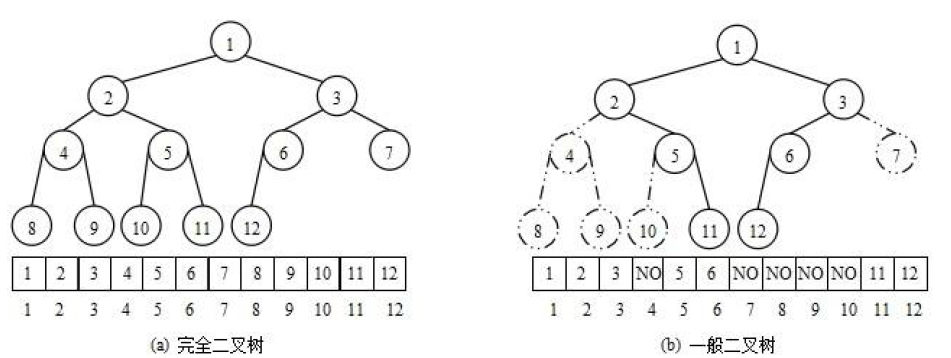
二叉树就是每个节点最多只有两颗子树的树:
对于二叉树有:
满二叉树:所有的子节点都在最后一层,且节点总数与层数有
节点总数=2^n-1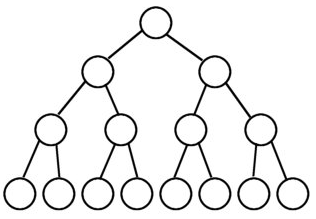
完全二叉树:从根节点到倒数第二层都符合满二叉树,但是最后一层节点不完全充填,叶子结点都靠左对齐
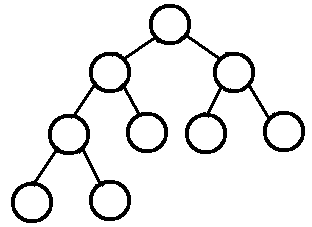
二、二叉树的遍历
二叉树遍历分为三种:
- 前序遍历: 先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
- 中序遍历: 先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
- 后序遍历: 先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
可见,根据父节点输出顺序即可以判断是哪一种遍历。
1.简单代码实现
先创建节点类:
1 | /** |
实现遍历方法:
1 | /** |
2.测试
对含有7个简单的满二叉树进行遍历的结果:
1 | 前序遍历: |
三、二叉树的查找
大体逻辑同遍历,这里就不在赘述了,直接放代码:
1 | /** |
四、二叉树的删除
对于二叉树的删除,有以下逻辑:
- 由于树的节点和节点之间的联系是单向的,对于要删除的节点,需要找到他的父节点进行删除
- 从根节点开始遍历节点,判断节点的左右子节点是否为目标节点
- 如果是就删除并返回
- 否则就持续向右或左递归,直到找到目标节点,或者将树遍历完为止
1 | /** |
五、顺序存储二叉树
一般想到二叉树都会先想到较为形象的链式存储,即用含有左右指针的节点来组成树,实际上,通过计算,也可以使用数组来表示二叉树。
可以简单的理解:顺序存储二叉树是逻辑的上一棵树,而链式存储二叉树是物理上的一棵树。
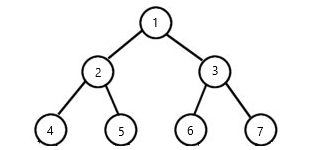
以下图的树为例:

假设数组为{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,},我们可以知道:
- 下标为n的元素的左节点为:
2*n+1 - 下标为n的元素的右节点为:
2*n+2 - 下标为n的元素的父节点为:
(n-1)/2
如果给顺序存储二叉树写一个前序遍历急就是这样:
1 | /** |
在代码的实现上和链式二叉树是差不多的,这里就不再一一列举了。
当然,由于顺序存储二叉树的性质,当树需要排序的情况下,顺序存储二叉树就会出现空间浪费的情况: