前言
我们知道,spring 的启动其实就是容器的启动,而一般情况下,容器指的其实就是上下文 ApplicationContext。
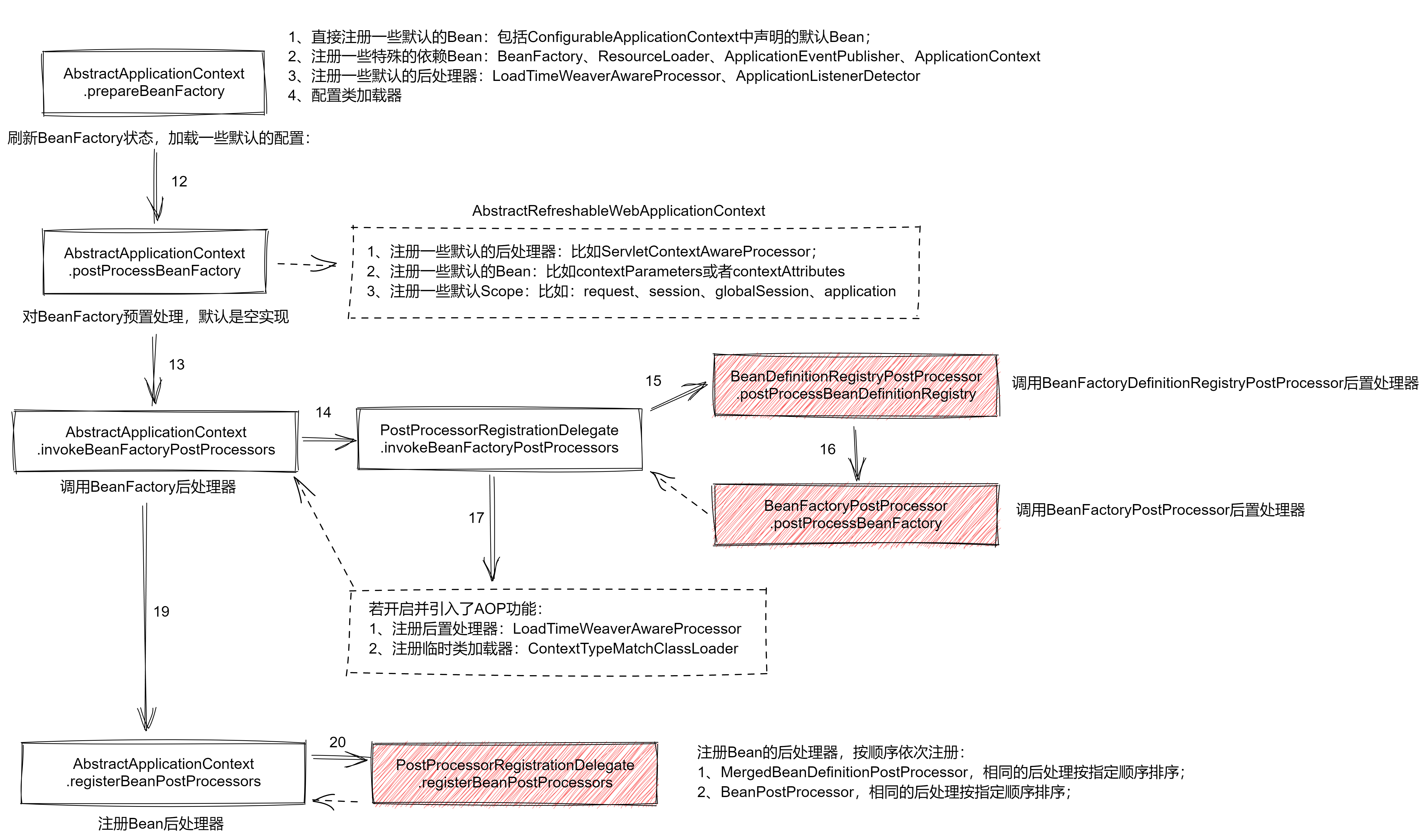
AbstractApplicationContext 作为整个 ApplicationContext 体系中最高级的抽象类,为除了 ComplexWebApplicationContext 和 SimpleWebApplicationContext 这两个容器外的全部容器,规定好了 refresh 的整体流程,所有的容器在完成一些自己的初始化配置后,都需要调用该 refresh 方法,依次完成指定内容的初始化。
也就是说,读懂了 AbstractApplicationContext.refresh() 方法,其实就读懂了容器的启动流程:
1 | public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { |
从总体来看,该方法描述的初始化过程大概分为三步:
- [x] 上下文的初始化;
- [x]
BeanFactory初始化; - [ ] 事件,Bean及其他配置的初始化;
笔者将基于 spring 源码 5.2.x 分支,分别通过五篇文章从源码分析 spring 容器的初始化过程。
本文是其中的第二篇文章,将介绍 BeanFactory 初始化。
相关文章:
-
一、对工厂进行默认后置处理
AbstractApplicationContext.postProcessBeanFactory()是BeanFactory的第一步,该过程用于在用户自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor前,对BeanFactory进行一些默认的配置。在
AbstractApplicationContext中,这个方法是个空实现,需要子类实现它的具体逻辑,但是无外乎都是做以下三件事:- 向
BeanFactory注册默认的Bean后置处理器; - 向
BeanFactory注册默认的Bean作用域; - 向
BeanFactory注册一些默认的Bean;
我们以一个典型的实现类
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext为例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 注册后置处理器ServletContextAwareProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);
// 注册web环境下一些必要组件
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}1、注册默认Bean后置处理器
postProcessBeanFactory()最先调用了BeanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor()用于注册ServletContextAwareProcessor这个Bean后置处理器:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16// beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor
public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null");
// Remove from old position, if any
this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);
// Track whether it is instantiation/destruction aware
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
// Add to end of list
this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);
}而对于
ServletContextAwareProcessor这个类,我们只需要关注它实现的postProcessBeforeInitialization接口:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (getServletContext() != null && bean instanceof ServletContextAware) {
((ServletContextAware) bean).setServletContext(getServletContext());
}
if (getServletConfig() != null && bean instanceof ServletConfigAware) {
((ServletConfigAware) bean).setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
}
return bean;
}它将向所有实现了
ServletConfigAware的 bean 注册ServletContext和ServletConfig这两个 bean,这也是为什么要在postProcessBeanFactory中1
2beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);忽略
ServletContextAware和ServletConfigAware的原因了,因此ServletContextAwareProcessor已经完成了这两者的功能。2、注册默认Bean作用域
registerWebApplicationScopes方法主要用于注册request,session,globalSession,application这四个作用域:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
ServletContext sc) {
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, new RequestScope());
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, new SessionScope());
if (sc != null) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc);
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope);
// Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it.
sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
}
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
if (jsfPresent) {
FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory);
}
}3、注册默认Bean
registerEnvironmentBeans方法用于注册contextParameters和contextAttributes这两个环境 bean:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44public static void registerEnvironmentBeans(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf,
ServletContext servletContext, ServletConfig servletConfig) {
if (servletContext != null && !bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME)) {
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME, servletContext);
}
if (servletConfig != null && !bf.containsBean(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME)) {
bf.registerSingleton(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME, servletConfig);
}
if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME)) {
Map<String, String> parameterMap = new HashMap<>();
if (servletContext != null) {
Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletContext.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement();
parameterMap.put(paramName, servletContext.getInitParameter(paramName));
}
}
if (servletConfig != null) {
Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement();
parameterMap.put(paramName, servletConfig.getInitParameter(paramName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(parameterMap));
}
if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME)) {
Map<String, Object> attributeMap = new HashMap<>();
if (servletContext != null) {
Enumeration<?> attrNameEnum = servletContext.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNameEnum.nextElement();
attributeMap.put(attrName, servletContext.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(attributeMap));
}
}二、使用后处理器对工厂进行处理
在调用完
AbstractApplicationContext.postProcessBeanFactory()后,BeanFactory中已经具备了一些 spring 默认的配置,此时再调用AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,使用用户提供的工厂后置处理器BeanFactoryPostProcessor对BeanFactory进行后置处理。在
AbstractApplicationContext中,该方法实现如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 借助后处理委托类调用全部的后置处理器
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// 如果存在loadTimeWeaver这个bean,则会配置上LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor这个后置处理器
// 然后设置临时的类加载器ContextTypeMatchClassLoader
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
// AbstractApplicationContext
public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {
return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors; // 这些是直接注册到上下文中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
}这里其实主要分为两部分逻辑:
- 借助后处理器委托类
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate完成对BeanFactory的后置处理; - 如果引入了
AOP,则需要为BeanFactory设置特殊的类加载器,从而允许生成Bean时织入切面逻辑;
第二部分很简洁,主要的逻辑都在第一部分。
1、后处理委托类
这里又出现了一个新类
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate,该类实际上是一个静态工具类,专门提供静态方法以用于处理上下文的后处理操作的,该类总共提供了两个方法:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors():该方法用于对BeanFactory进行后置处理;registerBeanPostProcessors():该方法用于向上下文中注册Bean的后置处理器;
2、对BeanFactory进行后处理
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()这个方法非常的长,不过逻辑还是很明确的:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
// 如果BeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
// 将后置处理器分为两类:
// 1.普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
// 2.BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 若是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,则先调用该类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 先调用实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 再调用实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 最后调用没实现PriorityOrdered或者Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// 如果BeanFactory没有实现BeanDefinitionRegistry接口
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 过滤掉已经调用过的处理器,然后把处理器分为三类:
// 1.实现了PriorityOrdered接口的处理器;
// 2.实现了Ordered接口的处理器;
// 3.没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的处理器;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 调用实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 调用实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 调用没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的后置处理器
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 清除元数据
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}由于
BeanFactoryPostProcessor存在一个子接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,它对应BeanFactory的一个子实现BeanDefinitionRegistry,通过BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor可以调整实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry的BeanFactory中对Bean定义的一些信息。由于
Bean的定义肯定要比Bean的创建更优先,因此需要先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,然后再执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor。同时,又由于 spring 提供了一套排序机制,即处理时优先处理实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的处理器,再处理实现了Ordered接口的处理器,最后再处理两个接口都不实现的处理器,执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,与执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor时都还要根据排序区分执行顺序。因此,综合上文,这一步总体流程其实是这样的:
- 若
BeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,则优先完成此步骤:- 先调用实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; - 再调用实现了
Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; - 最后调用没有实现上述两接口的
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
- 先调用实现了
- 不管是否实现了
BeanDefinitionRegistry,都完成此步骤:- 先调用实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor; - 再调用实现了
Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor; - 最后调用没有实现上述两接口的
BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
- 先调用实现了
三、注册Bean后处理器
AbstractApplicationContext.registerBeanPostProcessors()是BeanFactory加载的第三步。这一步与调用BeanFactory一样,都通过后置处理委托类PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate进行:1
2
3protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}1、注册后处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors与 上文调用BeanFactory后置处理器逻辑基本一致:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// 依然将后置处理器分为三类:
// 1.实现了PriorityOrdered接口的处理器;
// 2.实现了Ordered接口的处理器;
// 3.没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的处理器;
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
// 这里是用于框架内部使用的后置处理器
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// 注册实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// 注册没有实现PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的后置处理器
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// 注解框架内部使用的后置处理器
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// 重新注册ApplicationListenerDetector,保证该处理器总是位于处理器链的最后一位,从而总是在最后被执行
// 该后置处理器用于支持spring的事件机制
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}上述这些代码的逻辑也很明确:
- 先注册实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor; - 再注册实现了
Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor; - 接着注册没有实现上述两接口的
BeanPostProcessor; - 然后再注册框架内部使用的
BeanPostProcessor; - 最后注册
ApplicationListenerDetector,保证该后置处理器总是位于处理器链的末尾;
2、后处理器之间的优先级
在这一步,我们能看到,
BeanPostProcessor之间也会根据优先级区分创建 & 注册顺序,因此也就有了两个有意思的情况:- 后处理器本身也是一个
Bean,因此后处理创建时也会被后处理; - 后创建的后处理会被先创建的后处理器进行后处理;
基于上述两点,我们就可以理解,为什么有些
Aware本身就需要由后处理调用,但是仍然有别的后处理回去实现这些Aware接口,因为这些实现了接口的后处理本身也是一种Bean,也可以被先注册的后处理器进行处理。总结
当上下文刷新完毕,并且准备好了新的
BeanFactory后,需要对BeanFactory进行三步操作以完成BeanFactory本身的初始化:-
postProcessBeanFactory:对 bean 工厂进行预处理,包括注册一些默认的Bean后置处理器,设置默认的Bean作用域,以及注册默认Bean等; -
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:使用注册到上下文中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor与BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor对BeanFactory进行后置处理; -
registerBeanPostProcessors:注册 bean 的后处理器,包括用户自定义的、spring 内部使用的,以及用于支持事件机制的ApplicationListenerDetector;
- 向