概述
Java 8 API添加了一个新的抽象称为流Stream,可以让你以一种声明的方式处理数据。
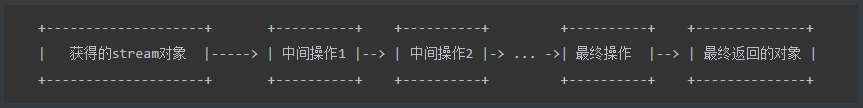
这种风格将要处理的元素集合看作一种流, 流在管道中传输, 并且可以在管道的节点上进行处理, 比如筛选, 排序,聚合等。
元素流在管道中经过中间操作的处理,最后由最终操作得到前面处理的结果。
二. 举个例子?
现在有一个字符串集合,我们需要过滤掉集合里头长度小于2的字符串:
1 | public static void main( String[] args ) { |
如果使用stream实现一模一样的效果:
1 | public static void main( String[] args ) { |
可见,使用streamAPI可以轻松写出更高效,更简洁,可读性更强的代码
三. 如何使用stream?
简单的说,分两步:生成流,操作流
1. 生成流
Stream 的创建需要指定一个数据源,比如 java.util.Collection的子类,List或者Set, 不支持Map
1.1 Collection接口的stream()或parallelStream()方法
1 | //将Set或List集合直接转换为stream对象 |
1.2 Stream.of(),Arrays.stream,Stream.empty()方法
1 | String[] strArr = {"a","a","a","a","a","a"}; |
1.3 Stream.concat()方法
1 | //已有的对象 |
1.4 静态的Files.lines(path)
1 | File file = new File("D://test.txt"); |
2. 操作流
Stream 操作分为中间操作或者最终操作两种,最终操作返回一特定类型的计算结果,而中间操作返回Stream本身,可以在后头跟上其他中间操作
1 | //接下来的示例代码基于此集合 |
2.1 filter(Predicate:将结果为false的元素过滤掉
1 | //去掉长度小于2的字符串 |
2.2 map(fun):转换元素的值,可以引用方法或者直接用lambda表达式
1 | strings = strings.stream() |
2.3 limit(n):保留前n个元素
1 | strings = strings.stream() |
2.4 skip(n):跳过前n个元素
1 | strings = strings.stream() |
2.5 distinct():剔除重复元素
1 | strings = strings.stream() |
2.6 sorted():通过Comparable对元素排序
1 | strings = strings.stream() |
2.7 peek(fun):流不变,但会把每个元素传入fun执行,可以用作调试
1 | strings = strings.stream() |
2.8 flatMap(fun):若元素是流,将流摊平为正常元素,再进行元素转换
1 | //将具有多重嵌套结构的集合扁平化 |
2.9 anyMatch(fun),allMatch(fun):判断流中的元素是否匹配 【最终操作】
1 | //allMatch |
2.10 forEach(fun): 迭代流中的每个数据 【最终操作】
1 | strings.stream() |
2.11 collect():返回结果集 【最终操作】
1 | strings = strings.stream() |
四. 使用IntSummaryStatistics类处理数据
1. IntSummaryStatistics类
IntSummaryStatistics类,在 java8中配合Stream使用,是用于收集统计信息(例如计数,最小值,最大值,总和和*平均值)的状态对象。
这个类长这样:
1 | public class IntSummaryStatistics implements IntConsumer { |
2.使用
这个类的理解起来很简单,内部有这几个方法:
2.1 获取总条数:getCount(),
2.2 获取和:getSum(),
2.3 获取最小值:getMin(),
2.4 获取最大值:getMax(),
2.5 获取平均值:getAverage()
示例如下:
1 | public static void main( String[] args ) { |